These two main belt asteroids have similar obit parameters.
Their orbit condition codes are 1 and 0 respectively
Using the JPL Small-Body Database Browser, we can see:
470785 (2008 UX299)
| Classification: Main-belt Asteroid SPK-ID: 2470785 |
| [ Ephemeris | Orbit Diagram | Orbital Elements | Physical Parameters | Discovery Circumstances ] |
[ show orbit diagram ]
| Orbital Elements at Epoch 2458000.5 (2017-Sep-04.0) TDB Reference: JPL 8 (heliocentric ecliptic J2000)
| Orbit Determination Parameters
Additional Information
|
233771 (2008 TO124)
| Classification: Main-belt Asteroid SPK-ID: 2233771 |
| [ Ephemeris | Orbit Diagram | Orbital Elements | Physical Parameters | Discovery Circumstances | Close-Approach Data ] |
[ show orbit diagram ]
| Orbital Elements at Epoch 2458000.5 (2017-Sep-04.0) TDB Reference: JPL 8 (heliocentric ecliptic J2000)
| Orbit Determination Parameters
Additional Information
|
I tried to simulate their behavior in the past to investigate whether they might be related.
Simulation set-up
Mercury6 Integrator
reference:
J.E.Chambers (1999)
A
Hybrid Symplectic Integrator that Permits Close Encounters between
Massive Bodies''. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, vol
304, pp793-799.
Integration parameters----------------------
Algorithm: Bulirsch-Stoer (conservative systems)
Integration start epoch: 2458000.5000000 days
Integration stop epoch: -100000000.0000000
Output interval: 100.000
Output precision: medium
Initial timestep: 0.050 days
Accuracy parameter: 1.0000E-12
Central mass: 1.0000E+00 solar masses
J_2: 0.0000E+00
J_4: 0.0000E+00
J_6: 0.0000E+00
Ejection distance: 1.0000E+02 AU
Radius of central body: 5.0000E-03 AU
In
order to perform the simulation I generated 30 clones for each
asteroids (same average orbital parameters as the nominal ones and
standard deviation almost about the one calculated by JPL).
Thus, I evaluated 900 couples to check whether there was a moment in the past when two clones were very near with a very low relative velocity.
In particular, I used two arbitrary thresholds to detect interesting couples:
- distance less than 1 Lunar Distance - about 0.0020 AU
- relative velocity less than 1 m/s
The clone generation and the couples evaluation have been done using scripts written in R.
Simulation Results
The results are interesting because 819 out of 900 couples satisfy the thresholds mentioned above.
Distance between clones (km):
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. sd
105 1200 2190 3270 3230 119000 9030
Relative velocity (m/s) when at minimum distance:
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. sd
0.034 0.092 0.120 0.140 0.150 0.940 0.09
Time of minimum distance (Years):
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. sd
-272820 -75850 -62761 -74560 -56070 -18177 41444
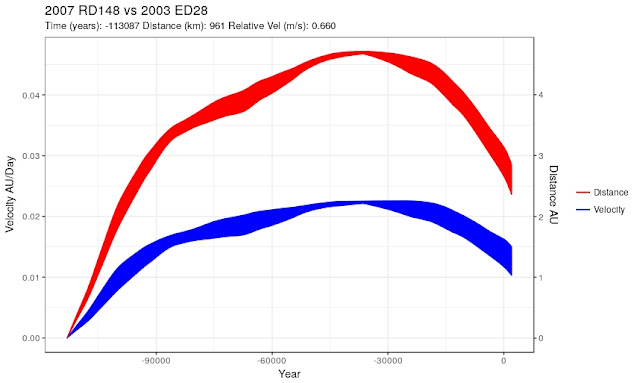
In a graphical form:
same as above but with a little more "zoom" ...:
The couple that went very near
Note that the time step is 100 days (this is consistent with a physical separation):
Conclusion
While this does not prove that the asteroids originated from a common body, it seems that this is certainly a possibility.
Kind Regards,
Alessandro Odasso